Unraveling the Connection: BMS and COVID-19
As we navigate the evolving landscape of the COVID-19 pandemic, we're beginning to uncover its multifaceted impact on health, far extending beyond the respiratory system. I'm Dr. Shane Cope, and at Essential Sprays, we've observed an unexpected pattern: a rise in cases of Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) among those who have recovered from COVID-19. This concerning trend prompts a closer look at the potential connection between a viral infection primarily known for affecting the lungs and a complex oral condition characterized by a persistent burning sensation in the mouth.
BMS typically manifests with discomfort that can affect the tongue, lips, or entire mouth, often accompanied by taste disturbances and dry mouth. While the direct cause of BMS can be elusive, its association with viral infections isn't unprecedented. However, the link with COVID-19 brings new challenges and questions to the fore.
In this blog, we'll delve into the symptoms of BMS, how they may intersect with post-COVID health issues, and what that means for those affected. We'll also explore how Essential Sprays is playing a role in providing relief during these times of uncertainty, with a focus on our All Natural Dry Mouth Spray, which has been a source of comfort for many BMS sufferers.
As we seek to unravel the connection between BMS and COVID-19, one thing remains clear: the importance of addressing oral health as a key component of overall well-being, especially in the wake of this global health crisis.
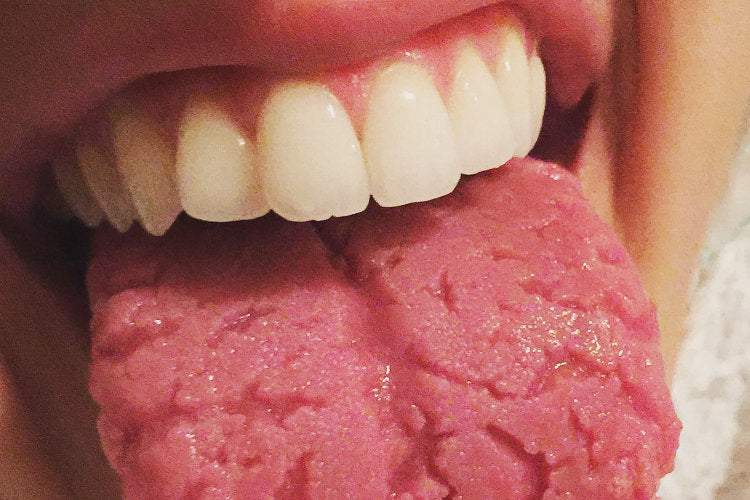
Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) Explained:
BMS is a distressing condition characterized by a chronic burning sensation in the mouth, often without any visible signs or medical cause. This perplexing disorder primarily affects the tongue, but it can also involve the lips, gums, palate, or entire mouth. Typical symptoms include a persistent feeling of scalding or tingling, dry mouth (xerostomia), altered taste sensations, and sometimes increased thirst. While the exact prevalence of BMS is hard to determine, it is known to affect a significant portion of the population, particularly middle-aged and older women. The impact of BMS on quality of life can be profound; the constant discomfort can interfere with eating, speaking, and sleeping, leading to frustration and emotional distress. The chronic nature of BMS, coupled with the challenge of finding effective treatment, often contributes to anxiety and depression in sufferers. Thus, BMS is not just a physical ailment; its psychological and emotional toll underscores the need for comprehensive care and support for those affected.
COVID-19 Overview:
COVID-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged as a global pandemic in early 2020. Characterized primarily by respiratory symptoms like cough, fever, and shortness of breath, it rapidly affected millions worldwide. However, COVID-19 also presents a range of less common symptoms. Among these, several pertain to oral health, including a loss of taste and smell, which has been widely reported. Additionally, some patients have experienced oral manifestations such as mouth sores, lesions, dry mouth, and an increased susceptibility to oral infections. These symptoms highlight the virus's impact beyond the respiratory system, affecting various bodily functions and overall health. Understanding the full scope of COVID-19's symptoms, including those related to oral health, remains crucial in its diagnosis and management.
Emerging Patterns: COVID-19 and Oral Health:
The emergence of COVID-19 has brought about a new understanding of its impact on oral health, with clinical observations and early research indicating significant changes post-infection. Healthcare professionals have noted a range of oral health issues in patients recovering from COVID-19, including an increase in cases of dry mouth and altered taste sensations. These changes are thought to result from the virus's effect on the salivary glands and taste buds. More notably, there has been a surge in anecdotal reports and preliminary studies suggesting a link between COVID-19 and increased instances of Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS). Patients who have recovered from COVID-19 have reported symptoms synonymous with BMS, such as persistent burning sensations in the mouth, dryness, and a metallic taste. While these observations are still in the early stages of research, they point to a potential new subset of post-COVID complications. The precise mechanism behind these oral health changes is not yet fully understood, but it is hypothesized that the virus's impact on the body's neurological and immune systems may play a role. This emerging pattern underscores the need for further studies to understand the full scope of COVID-19's effects on oral health and develop appropriate treatment strategies.
Potential Mechanisms Linking BMS and COVID-19:
The potential mechanisms linking Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) and COVID-19 delve into a complex interplay between viral infection, immune response, and nervous system involvement. The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, could potentially trigger BMS symptoms through its interaction with the body's immune and nervous systems. One hypothesis suggests that the virus might directly or indirectly affect the nerves responsible for sensation in the oral cavity, leading to the neuropathic pain characteristic of BMS. This could occur due to the virus infiltrating nerve tissues or through an immune-mediated response where the body's defense against the virus inadvertently damages peripheral nerves.
Additionally, the systemic inflammation triggered by a COVID-19 infection could contribute to the development of BMS symptoms. Inflammatory cytokines, released in response to the virus, might lead to alterations in the oral mucosal environment, potentially triggering the burning sensation experienced in BMS. This inflammatory response could also disrupt the normal functioning of salivary glands, leading to dry mouth, which is a common complaint among BMS sufferers.
Another possibility is that the psychological stress associated with COVID-19 — encompassing illness, social isolation, and general anxiety about the pandemic — might exacerbate or trigger BMS. Stress is known to affect pain perception and could contribute to the onset or worsening of BMS symptoms.
Understanding these potential mechanisms is vital for developing effective treatments and management strategies for BMS in the context of COVID-19. As research continues, these insights will be crucial in addressing the oral health challenges faced by those recovering from COVID-19.
Management Strategies for BMS in the COVID-19 Era:
In the COVID-19 era, managing Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) necessitates a nuanced approach, considering the unique challenges of post-COVID recovery. Individuals recovering from COVID-19 who are experiencing BMS symptoms should prioritize maintaining adequate hydration. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential, as it helps to alleviate the dry mouth often associated with BMS, and can reduce the burning sensation. Nutrition also plays a critical role; a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall oral health and potentially mitigate some BMS symptoms. It's advisable to avoid foods and beverages that might exacerbate BMS symptoms, such as spicy and acidic foods, and those high in sugars.
Stress management is another key component of BMS management in the post-COVID context. The pandemic has brought about significant stress and anxiety, which can exacerbate BMS symptoms. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and counseling can be beneficial in managing stress. Gentle oral hygiene practices, using products that are non-irritating and alcohol-free, can also help in minimizing discomfort.
Moreover, consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans is crucial. This might include the use of specific oral rinses, medications to manage pain, or therapies to address nerve sensitivity. Given the potential link between COVID-19 and BMS, patients should inform their healthcare providers about their COVID-19 history to tailor the treatment plan effectively.
In summary, managing BMS in the COVID-19 era involves a holistic approach that includes hydration, nutrition, stress management, and specialized medical care, recognizing the complex interplay between post-COVID recovery and BMS symptoms.
The Role of Healthcare Providers:
The role of healthcare providers is pivotal in managing Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS), particularly in the context of post-COVID recovery. Individuals experiencing persistent BMS symptoms post-COVID are strongly encouraged to seek professional medical advice. Healthcare providers can offer a comprehensive assessment to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms, such as nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, or oral fungal infections. Given the complexity of BMS, particularly when linked to a recent COVID-19 infection, a multidisciplinary approach is often necessary for effective management. This approach may involve collaboration between dentists, general practitioners, neurologists, nutritionists, and mental health professionals.
Dentists play a crucial role in addressing any direct oral health issues, while general practitioners can oversee the overall management, including evaluating for systemic causes. Neurologists may be involved in cases where nerve dysfunction is suspected. Nutritionists can provide guidance on dietary adjustments to alleviate symptoms, and mental health professionals can offer support for the psychological impact of chronic pain and illness. This collaborative effort ensures a comprehensive treatment plan, addressing not just the physical symptoms but also the psychological aspects of BMS, enhancing the overall quality of care and patient outcomes. By seeking help from the appropriate healthcare providers, patients with BMS linked to COVID-19 can receive tailored treatments that address the multifaceted nature of their condition.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the potential link between Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) and COVID-19 underscores a critical area of concern in post-pandemic healthcare. As we continue to witness and study this association, it becomes increasingly clear that awareness and proactive management of BMS are essential, especially for those recovering from COVID-19. The complexity of BMS, with its multifactorial etiology and wide range of symptoms, calls for a thorough understanding and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. This understanding is vital not only for healthcare providers but also for patients who may be navigating the perplexing symptoms of BMS in the wake of COVID-19.
At Essential Sprays, we are deeply committed to supporting those suffering from BMS, recognizing the significant impact this condition can have on quality of life. Our dedication goes beyond providing effective products like our specialized dry mouth sprays; it extends into a commitment to offering resources, education, and support to those affected. Whether navigating BMS as a post-COVID symptom or as a standalone condition, our goal is to empower individuals with the knowledge, products, and support they need to manage their symptoms effectively and improve their overall well-being. We stand with the BMS community, reaffirming our commitment to being a part of their journey towards better oral health and comfort.
